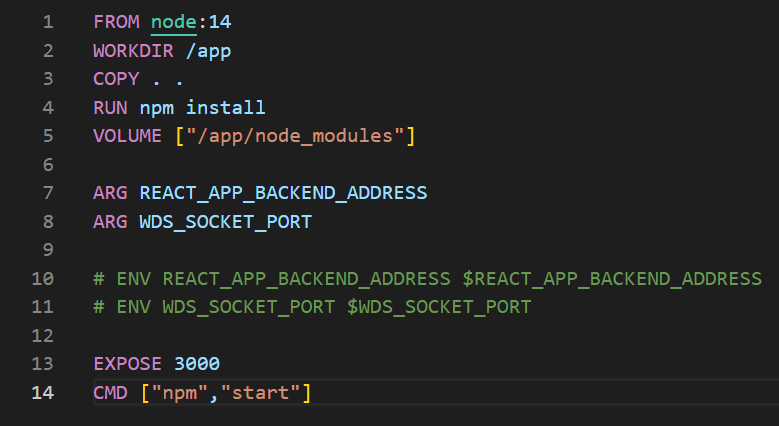
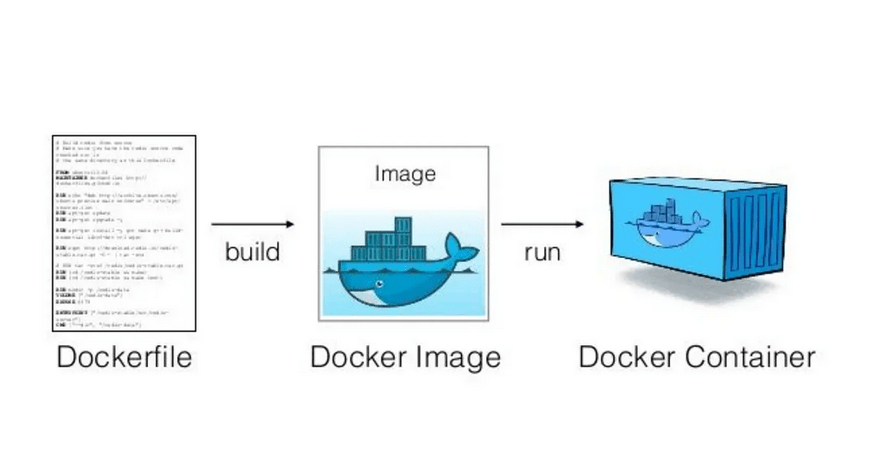
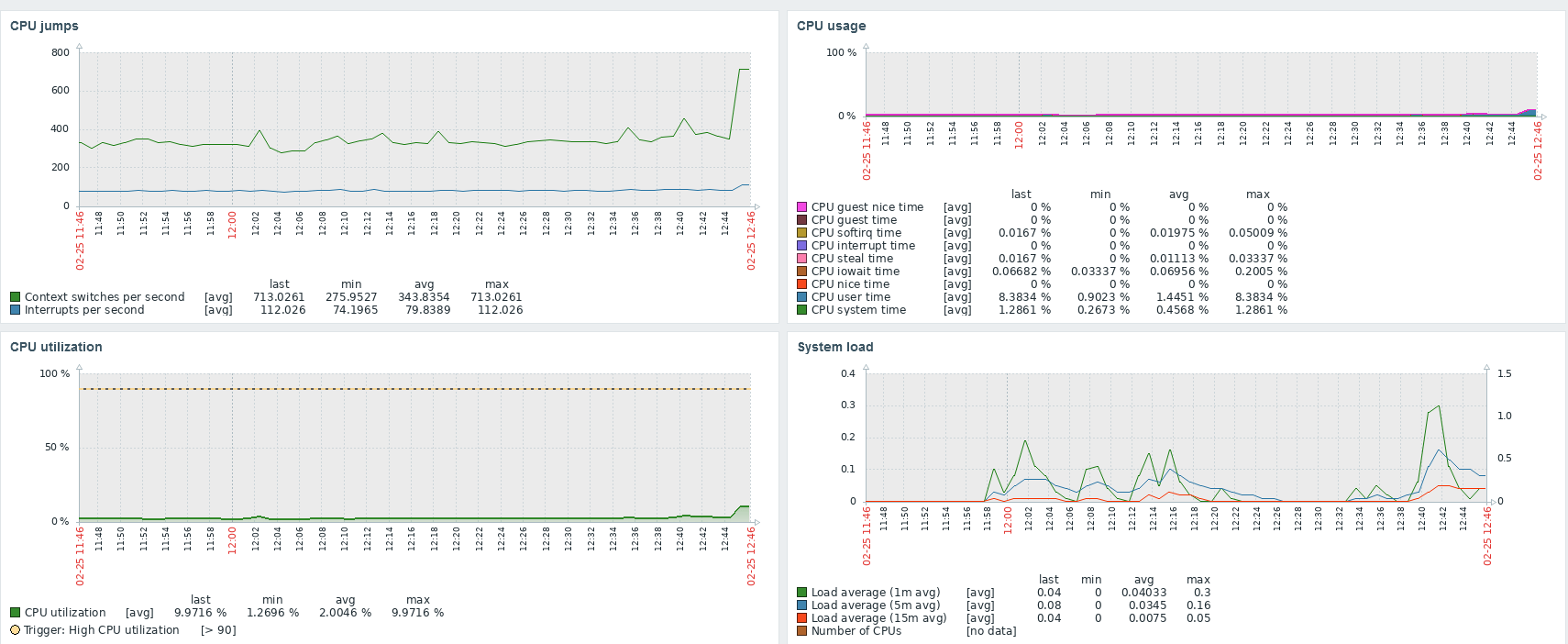
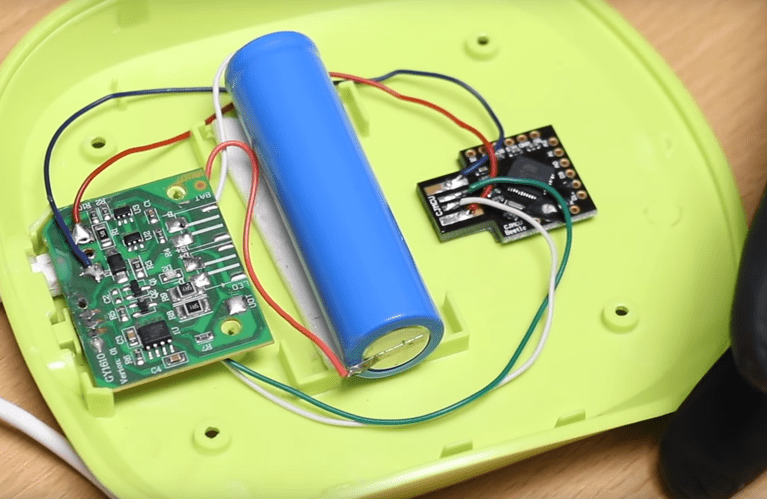
There exist many types of IT technology strategies, created for enterprises using different IT technologies, with different levels of advancement in the technology life cycle, with different external and internal conditions. One of the most common ways to determine an IT technology strategy model is through its selection, based on the following criteria [1]:
- Development potential of the IT field - meaning its value from the point of view of the future plans of the company,
- The company's presence on the market, measured by the degree of its market share, the size of the distribution network, market image, relations with market partners or brand recognition,
- The technological position of a company, measured by the degree of mastery of a given IT technology, considered important in the processes of competition and indicating the extent to which the company can build a strong competitive position thanks to it (the so-called key technology).
Assuming that the development potential of the IT field may be high or low (limited), and the market position and technological position may be strong or weak, a matrix has been developed which indicates how the operating strategies, including technological strategies, are to be adopted by an enterprise remaining in a specific technological situation (Tab. 1). Characterising the various situations in which an undertaking may find itself, the following can be stated.
- A company that operates in a field with high development potential, with a strong market and technological position, is in the most advantageous situation. The recommended technological strategy is to consolidate the market position and maintain or improve the technological position.
- The least favourable situation is for a company that operates in a field with limited or low development potential, with a weak market and technological position. The recommendations for the company in such a situation are to get rid of the business (IT technology) or to improve the profitability of the bases of additional capital expenditures, if possible.
In other cases, the situation of the company is more complex. - When the development potential of the field is low or limited – it is recommended to generate the highest possible liquidity (strong market and technological position), limited capital expenditures and purchase of technology, when it will immediately ensure adequate profitability (strong market position, weak technological position) or generate the highest possible liquidity, transfer activities to areas with higher development potential or making the technology available to partners who are able to make better use of it (weak market position, strong technological position in a given IT area).
- In the case of areas with high development potential, the directions of strategic action are indicated as market development in cooperation with a partner with a strong commercial base or resale of technology (weak market position, strong technological position), purchase of technology or acquisition and development of technological competence as soon as possible (strong market position, weak technological position) or investment of large funds to improve the market position and mastery of the technology or abandonment (weak market position, weak technological position).
Table 1. Models of IT technological strategies according to the development potential of the field and the market and technological position of the company
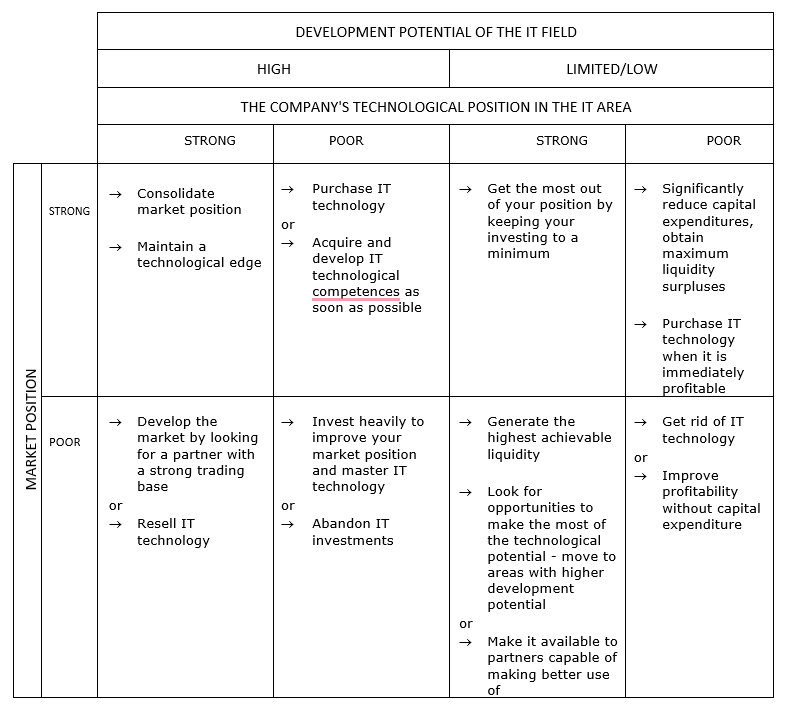
Source: In-house analysis based on: Strategor, company management. Strategies of Structure, Decisions, Identity, PWE, Warsaw 1995, pp. 151-154; S. Łobejko, Mission, strategy, innovation strategy [in:] A. Sosnowska + 5 Aut., How to implement technological innovations in a company. A guide for entrepreneurs, PARP, Warsaw 2005, pp. 36-37.
IT technology strategies are strongly linked to innovation. Hence, they can also be determined on the basis of the competitive position of products and the IT technology of their production, depending on the implementation of innovations (Characteristic. 1). In the case of a strong market and technological position, with the high importance of technology, the company can be ahead of competitors by maintaining technological and marketing leadership. With a strong technological position and a weaker market, it may be necessary to invest in improving marketing activity and strengthening market position. With a strong market position and uncompetitive technologies, the way to improve the situation would be to invest in technology development. The lack of market prospects and opportunities for technology development may mean that the company will have to withdraw from the market.
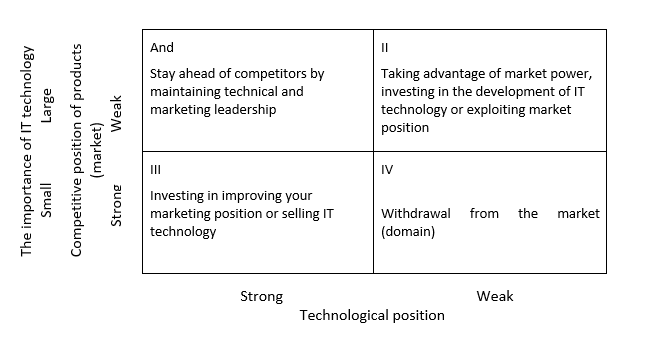
Characteristic. 1. Strategy for the development and commercialization of innovations
Source: S. Łobejko, Mission, strategy, innovation strategy, [in:] A. Sosnowska + 5 Aut., How to implement technological innovations in a company. A guide for entrepreneurs, PARP, Warsaw 2005, p. 38.
[1] Own elaboration based on: Strategor, Company management. Strategies of Structure, Decisions, Identity, PWE, Warsaw 1995, pp. 151-154; S.Łobejko, Mission, strategy, innovation strategy [in:] A.Sosnowska + 5 Aut., How to implement technological innovations in a company. A guide for entrepreneurs, PARP, Warsaw 2005, pp. 36-37.
Benefit from our experience and arrange a consultation on your business strategy! Click here.