Helm for the Second Time – Versioning and Rollbacks for Your Application
We describe how to perform an update and rollback in Helm, how to flexibly overwrite values, and discover what templates are and how they work.
 Author:
Author:Taking into account the impact of technology on the capabilities and performance of enterprises, especially those that base their market position on innovation, technology (including IT technologies) should be treated as one of the most important resources. This means that technologies and their development, like other key resources, must be taken into account in all the most important decisions regarding the current situation, and especially the future, in every enterprise that uses them. In today’s conditions of dynamic, vast, and varied changes in the environment, no organization is able to ensure sustainable, effective development, relying solely on current decisions and actions. In addition to operational management, focused on solving current problems, it’s necessary to prepare and implement decisions and actions of a forward-looking, long-term nature, referred to as strategic management.
Operational management is carried out in separate, relatively independent functional areas of the enterprise, defined as (Fig. 1):
In large enterprises, among the separated functional areas, there are also others (e.g. procurement and supplies), but such a situation occurs only when these areas are extremely important for the company’s operations.
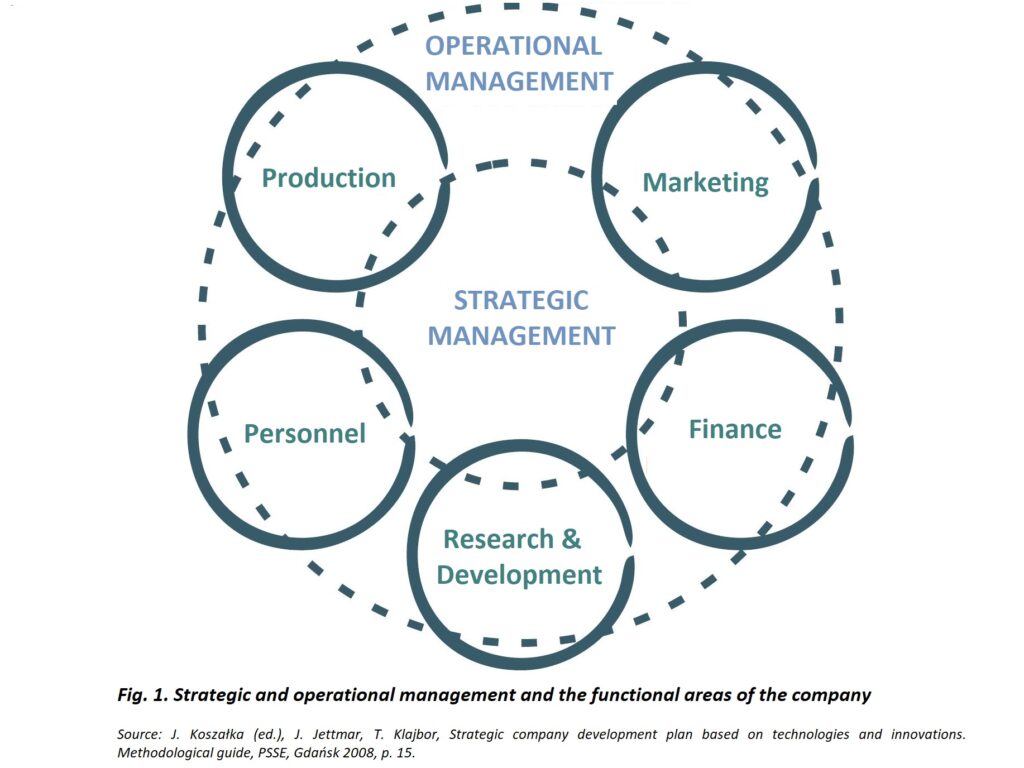
Strategic management resolves the key problems of survival and development of the company, taking into account the impact of the environment and its internal situation. Strategic activities are designed to answer three basic questions:
In short, starting from the current situation in the environment, strategic management defines what goals and how the enterprise should achieve in order to be in the desired situation in the planned period. Strategic management enables the company to achieve a competitive advantage on the market in the long term.
The main phases (stages) of the enterprise strategic management process include:
The business challenges and the company’s overall strategy indicate the general and specific goals of the business. Hence, in addition to the strategic goals and strategies of the entire company, many entities formulate goals and functional strategies that indicate the goals and methods of achieving them in all or some areas of activity.
In order to effectively manage technologies in a company, it is necessary to formulate long-term goals and strategies for IT technology, which can be an element of goals and strategies for the functional area “Research and development” (R&D). In shaping the technological strategy, the overall strategy of the company should be treated as paramount. On the one hand, when creating the company’s business strategy, one should take into account the state and conditions of activity in its functional areas, including R&D and technology. On the other hand, the technological strategy can be refined and effectively implemented, provided that the general strategy of the company is completed, taking into account the resulting guidelines or assumptions addressed to all functional areas, including R&D and technology.
For example, the business strategy of our company, INNOKREA, assumes, among others, building a continuous competitive advantage for our system for closed auctions (internalBID.com), which has been developed over about 4 years. Our technology strategy, in turn, supports this overall strategy, including usage of stable IT technologies (currently, e.g. React and React Native frameworks), ensuring high quality of our solutions for clients. Technologies change and / or are replaced by others (we wrote about it in Article#1).
In business practice, it is common and necessary to create interactions and constant feedback between technologies and business, while maintaining the hierarchy: the company’s strategy is superior to the technological strategy.

Helm for the Second Time – Versioning and Rollbacks for Your Application
We describe how to perform an update and rollback in Helm, how to flexibly overwrite values, and discover what templates are and how they work.
AdministrationInnovation

Helm – How to Simplify Kubernetes Management?
It's worth knowing! What is Helm, how to use it, and how does it make using a Kubernetes cluster easier?
AdministrationInnovation

INNOKREA at Greentech Festival 2025® – how we won the green heart of Berlin
What does the future hold for green technologies, and how does our platform fit into the concept of recommerce? We report on our participation in the Greentech Festival in Berlin – see what we brought back from this inspiring event!
EventsGreen IT